Symptoms of High Blood Sugar
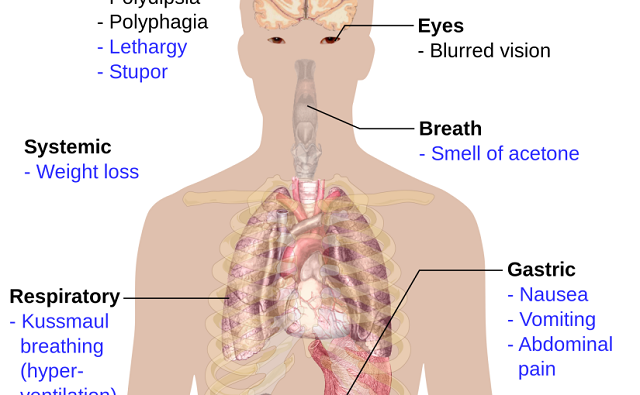
Symptoms of high blood sugar may be subtle but, if left untreated, they may harm your health. Glucose is the sugar fuel the body uses to power its cells. High blood sugar levels depend on how, when, and what you eat.
When the cells don’t properly absorb glucose, the symptoms of high blood sugar ultimately result in organ, nerve, and blood vessel damage. This sets the stage for extremely serious health complications.
Symptoms of High Blood Sugar
#1. You may have no symptoms.
Some people with high blood sugar levels don’t have apparent symptoms at first. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) says that millions of people have diabetes, but just one out of every four patients knows about it. About 86 million Americans have higher than average blood sugar counts, but they’re not high enough to result in a Type 2 diabetes diagnosis.
It’s important to get regular blood sugar tests if you’re at risk for diabetes. People above normal weight, those with hypertension, or people with a genetic predisposition to diabetes should ask their doctor to test their blood sugar levels on a regular basis:
- One high blood glucose reading won’t confirm a diabetes diagnosis. Blood sugar may spike if the individual is ill or under stress.
- Two or several elevated blood sugar tests can indicate diabetes.
If caught early, before additional symptoms of high blood sugar are present, it’s possible to treat diabetes and avoid the complications of diabetes later on.
#2. You drink, eat, and urinate a lot.
Too much blood glucose prompts the body to excrete it. Because excessive amounts of blood sugars spill into the urine, the individual urinates more often and may expel larger than usual amounts of urine:
- Too much blood glucose can eventually make the individual thirst. Dehydration occurs.
- Too much blood glucose may make others very hungry. Others experience rapid weight loss. The body’s cells aren’t receiving the glucose they need to operate.
Although some people don’t realize they’re diabetic until the doctor diagnoses the disease, others realize that urinary frequency, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, or hunger can result from diabetes.
#3. You’re exhausted.
When an individual’s cells don’t receive glucose, they’re actually starved of the fuel they need to function. This can make the diabetic feel exhausted:
- The diabetic’s blood becomes thick and viscous because high blood sugar causes the heart to work too hard.
- Thick blood can’t flow as easily to deliver energy to the cells.
- As the diabetic begins to urinate more frequently, he or she is flushing nutrients away.
- Thirst and urinary frequency cause sleep interruption as well.
#4. Your blood is viscous and syrupy.
Diabetic blood is thicker than non-diabetic blood. It’s more difficult for the blood to through the tiny blood vessels of the heart, eyes, kidneys, ears, and nervous system.
#5. High blood sugar can damage your vision.
High blood sugar levels serious affect eye health. Small blood vessel damage in the retina can cause blurred vision.
When blood sugar levels are in control, vision may improve. If the diabetic doesn’t control high blood sugar, it’s possible for abnormal blood vessels to appear. These obstruct the diabetic’s peripheral and central vision.
The center of the eye, the macula, can also swell when high blood sugar levels are present. Over time, this causes vision loss.
#6. You experience pain in your hands and feet.
Numbness in the fingers and toes is often a sign that blood sugar is too high. Peripheral neuropathy can occur over time. According to the American Academy of Neurology, long nerve fibers of the body are most easily affected by diabetes. For that reason, hands, feet, legs, and arms are vulnerable.
Nerve damage may produce pain, burning, or prickling. Controlling high blood sugar levels can help the diabetic to reverse damage or prevent new nerve damage.
#7. Your get more infections.
Individuals with high blood sugar may lose sensations in the feet. An injury, such as a blister or ingrown nail can become a big problem.
Because too much glucose in the blood feeds the wound, it can’t heal. Diabetics must protect themselves from infections. It’s essential to check the feet each day.
Unfortunately, diabetic foot ulcers or amputations are too common. To prevent these dire conditions, it’s essential to regulate blood sugar.
#8. Your sex life can be affected.
Diabetics sometimes notice erectile dysfunction or loss of libido. Female and male diabetics may fail to reach orgasm. Vaginal dryness or pain during intercourse may be symptoms of high blood sugar.
Because high blood sugar damages the blood vessels and nerves needed to facilitate sex, it’s important to control blood sugar.
#9. Your digestive system is out of whack.
Gastrointestinal problems may be a symptom of high blood sugar. Blood sugar problems may lead to a condition called <i>gastroparesis</i> which can affect the small intestine’s function. The diabetic may experience constipation, diarrhea, gastric pain, nausea, bloating, or vomiting.
#10. Your kidneys are damaged.
High blood glucose affects kidney function. The tiny blood vessels in the kidneys are needed to filter wastes from the bloodstream. If high blood sugar is present, the kidney’s filtration system must work harder to remove glucose from the blood. Over time, high blood sugar can scar the kidney’s filters.
Higher than normal protein in the urine is often the first sign of diabetic complications. It’s important to control high blood sugars and hypertension to preserve kidney function.
#11. Your brain and heart can be affected by high blood sugar.
Diabetics have higher risks of heart attack and stroke. Research shows this is the case even if the diabetic has identical cholesterol, blood pressure levels, and other factors associated with heart disease as non-diabetics.
Fortunately, research shows that good glucose control reduces the risks of heart disease, stroke, and death in diabetics. In addition, it may take a long period of time for high blood sugar levels to damage large vessels serving the brain and heart.
#12. Your memory may be affected by high blood sugar.
Doctors now believe that high blood sugar places diabetics at risk for memory problems, including Alzheimer’s disease. Some researchers believe that Alzheimer’s is <i>Type 3 diabetes.</i>
A European study showed that high blood sugar levels affect an individual’s memory over time. This can lead to circulatory problems, including poor memory, stroke, and brain atrophy.
#13. Your teeth and smile are affected.
High blood sugar is the enemy of a beautiful smile. Sugar in the saliva promotes dental caries and gum disease. Over a period of time, high blood sugar promotes painful or bloody gums, dry mouth and lips.
#14. You may suffer from bladder infections.
Diabetes bear a higher risk of bladder and urinary tract infections. Problems are typically more severe when an infection happens. Because high blood sugar damages nerves, the diabetic may experience an overactive bladder. It may be difficult to completely empty the bladder.
#15. Your skin becomes delicate and dry.
Diabetics often look older than their years. That’s because high blood sugar can affect the body’s biggest organ. As the diabetic’s body releases fluid, the skin is robbed of essential moisture. It’s dry and itchy. Fungal infections can appear in the groin or beneath the breasts.